Things to Know About World Bank
The World Bank is an internationally supported bank that provides financial and technical assistance to developing countries to aid their economic advancement with the stated goal of reducing poverty. It is one of the world’s largest sources of funding and knowledge for developing countries.
Facts on World Bank for SSC & Banking Exams –
⇒ President: Jim Yong Kim (12th)
⇒ Membership: 189 countries (IBRD), 173 countries (IDA)
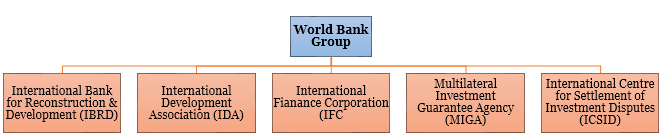
⇒ Affiliates: IFC, MIGA, ICSID
⇒ Headquarters: Washington, DC and more than 100 country staff about 10000 all over the world
⇒ The World Bank was conceived in 1944 to finance reconstruction of Europe
⇒ Authorized Capital: $ 184 Billion
The World Bank is the outcome of the Bretton Woods Conference, held in 1944. It was launched alongside the International Monetary Fund (IMF), in the presence of a number of important world delegates, and many important policymakers from the United States of America
Objectives of World Bank –
- To provide long-run capital to member countries for economic reconstruction and development
- To induce long-run capital investment for assuring Balance of Payments (BoP) equilibrium and balanced development of international trade
- To provide guarantee for loans granted to small and large units and other projects of member countries
- To ensure the implementation of development projects so as to bring about a smooth transference from a war-time to peace economy
- To promote capital investment in member countries by the following ways –
- To provide a guarantee on private loans or capital investment.
- If private capital is not available even after providing a guarantee, then IBRD provides loans for productive activities on considerate conditions.
Functions of World Bank –
- The Bank Group uses financial resources and extensive experience to help poor nations reduce poverty, increase economic growth, and improve the quality of life.
- Granting reconstruction loans to war-devastated countries
- Granting developmental loans to underdeveloped countries
- Providing loans to governments for agriculture, irrigation, power, transport, water supply, educations, health, etc.
- Providing loans to private concerns for specified projects
- Promoting foreign investment by guaranteeing loans provided by other organisations
- Providing technical, economic and monetary advice to member countries for specific project
- Encouraging industrial development of underdeveloped countries by promoting economic reforms
Purpose of the World Bank –
- Reduce poverty.
- Develop an investment-environment.
- Increase job opportunities.
- Work towards sustainable economic growth.
- Promote socio-economic growth through investment.
- Strengthen governments with education.
- Empower the development of legal and judicial systems, business opportunities and protection of individual rights.
- Benefit from microcredit as well as large corporate undertakings.
- Combat corruption.
- Promote research and training opportunities
- Provides low-interest loans,
- Interest-free credits
- Grants to include investments in education, Health, Public Administration, Infrastructure,
- Financial and private sector development,
- Agriculture, Environmental and natural resource management.
World Bank focuses on the achievement of the Millennium Development
Goals that call for the elimination of poverty and sustained development.
Millennium Development Goals –
The Millenium Development Goals are based on the 5 Key Factors –
- Build capacity
- Infrastructure creation
- Development of financial systems
- Combating corruptions
- Research, consultancy and Training
Areas of Operation of World Bank –
| Agriculture & Rural Development |
Labor & Social Protections |
| Conflict and Development |
Law & Justice |
| Development Operations & Activities |
Macroeconomic & Economic Growth |
| Economic Policy | Mining |
| Education | Poverty Reduction |
| Energy | Poverty |
| Environment | Private Sector |
| Financial Sector | Public Sector Governance |
| Gender | Rural Development |
| Governance | Social Development |
| Health, Nutrition & Population |
Social Protection |
| Industry | Trade |
| Information & Communication Technologies |
Transport |
| Information Computing & Telecommunications |
Urban Development |
| International Economics & Trade |
Water Resources |
| Water Supply & Sanitation | |
The World Bank & India –
- India was one of the 17 countries which met in Atlantic City, USA in June 1944 to prepare the agenda for the Bretton Woods conference
- In fact, the name “International Bank for Reconstruction and Development” [IBRD] was first suggested by India to the drafting committee
- The Bank lending to India started in 1949 when the first loan of $34 million was approved for the Indian Railways
- The aggregate of the Bank’s lending in India in the last 45 years was approximately $42 billion
- India is the single largest borrower of WB and IDA
- The World Bank Group’s Partnership Strategy for India (2013-2017) will help India lay the foundations for achieving “faster, sustainable, and more inclusive growth” as outlined in the government’s 12th five-year plan
- The World Bank Group will support India with an integrated package of financing, advisory services, and knowledge. During the World Bank financial year (July 2013-June 2014), funding for India was $5.2 billion ($2.0 billion in International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD), $3.1 billion in International Development Association and $0.1 billion in CTF or Clean Technology Fund) across 16 projects.
Criticism towards the World Bank –
- Promoting Washington consensus and allow only big corporations to flourish
- Ignore the environmental and social impact of projects
- Resentment and social turmoil in India
- Cause high debt amongst the countries
- Working with private sector will lead to decrease in the role of the state as primary provider
- Decisions are made and policies implemented by leading industrialized countries